\[ \dfrac{-R{T_2} \ln K_2}{T_2} - \dfrac{-R{T_1} \ln K_1}{T_1} = \Delta H^o \left(\dfrac{1}{T_2} - \dfrac{1}{T_1} \right) \nonumber \] And simplifying the expression so that only terms involving \(K\) are on the left and all other terms are on the right results in the van 't Hoff equation , which describes the temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant.. The van't Hoff factor is therefore a measure of a deviation from ideal behavior. The lower the van 't Hoff factor, the greater the deviation. As the data in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) show, the van't Hoff factors for ionic compounds are somewhat lower than expected; that is, their solutions apparently contain fewer particles than predicted by the number of ions per formula unit.

The van't hoff factor (i) for a dilute aqueous solution of the strong electrolyte barium
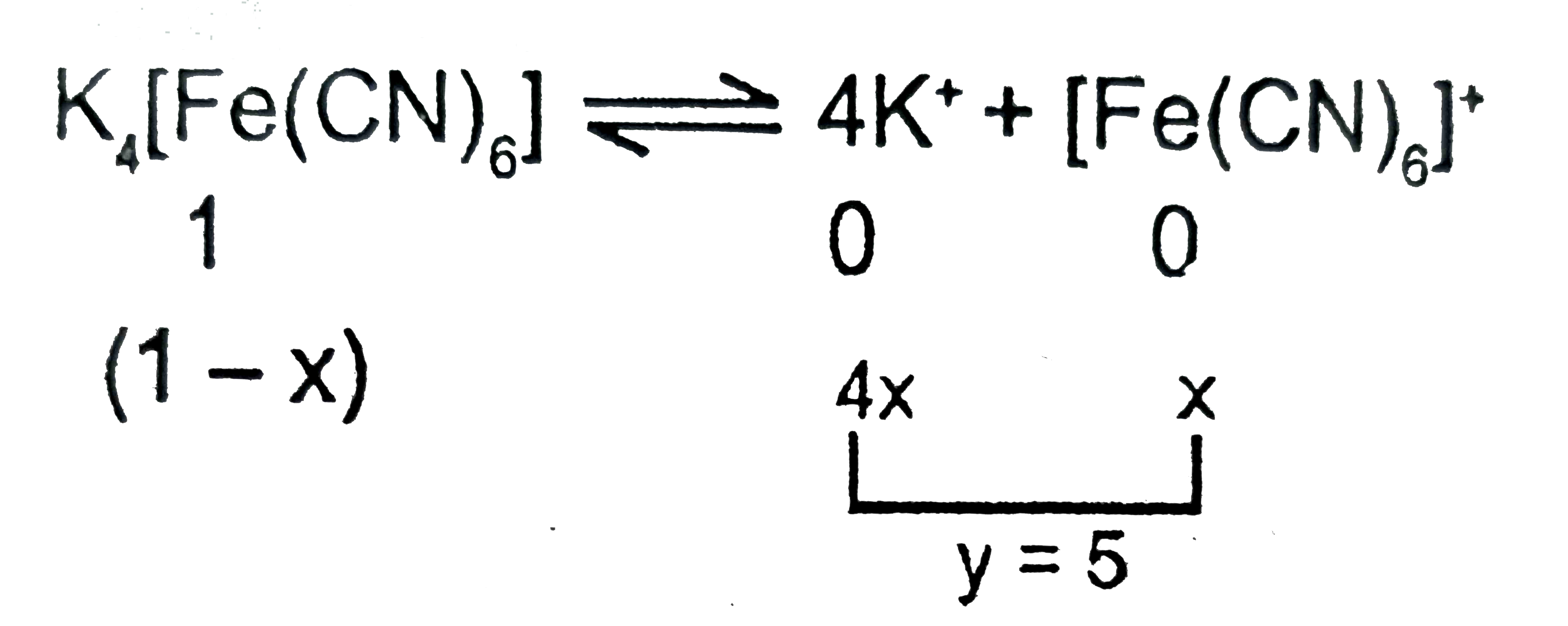
What is van't Hoff factor in each of the following cases? (A) Aq. K(

CHEM 201 Calculating Actual van't Hoff Factor YouTube

Ecuación de VAN'T HOFF ejercicio resuelto (ejemplo 2) YouTube

van't Hoff i factor of representative compounds. Download Scientific Diagram
Equilibrio químico. Constante de equilibrio y temperatura. Ecuación de Van't Hoff YouTube

Van’t Hoff Factor Definition, Formula, and Examples

Understanding vant hoff factor part 2 YouTube

The van't Hoff Factor Definition and How to Calculate It

PPT COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5076143
.PNG)
Colligative Properties of Solutions Presentation Chemistry

The Van't Hoff Factor YouTube

Freezing Point of an Electrolyte and the van’t Hoff Factor YouTube
Van T Hoff Equation Calculator

Van't Hoff Factor explained in 5 min Unacademy Atoms Paaras Thakur YouTube

The van't Hoff plot and thermodynamic parameters of 2?ROTAHSA complex... Download Scientific

Chapter 13 Solutions Vodcast Van't Hoff Factor YouTube

VANT HOFF FACTOR CLASS 12TH CHEMISTRY BY AMIT SIR YouTube

Van't Hoff factor as a function of concentration (calculated according... Download Scientific
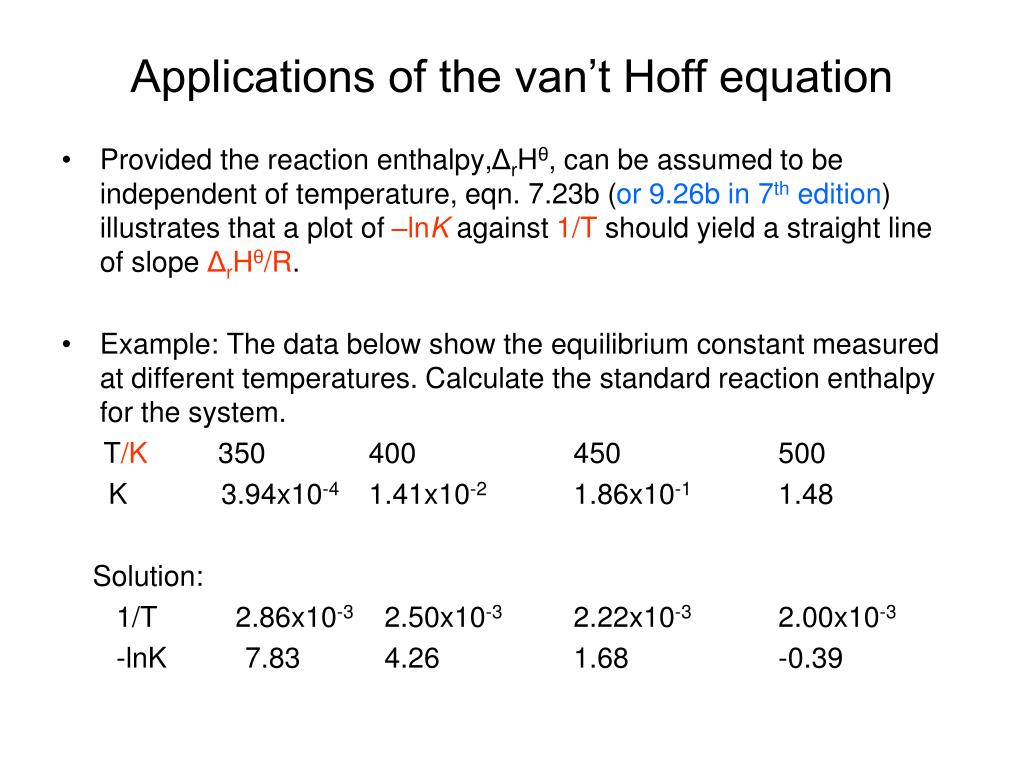
PPT Applications of the van’t Hoff equation PowerPoint Presentation ID2976187
the van't Hoff factor. The van't Hoff factor is really just a mathematical factor that scales the mixed or label concentration of a solute so that it matches the actual or total concentration of all species generated by that solute after dissolution. Solutes generally come in three types that we are concerned with: non-electrolytes, weak.. The Van't Hoff Factor of a covalently bonded compound is thus usually \(1\), because the result when the chemical is "dissociated" is one molecule, the one that was initially present. Example 1: The chemical 1-ethanol, with a structural formula \(CH_2OHCH_3\) and molecular formula \(C_2H_6O\), is a nonelectrolyte and does not dissociate in aqueous solution.