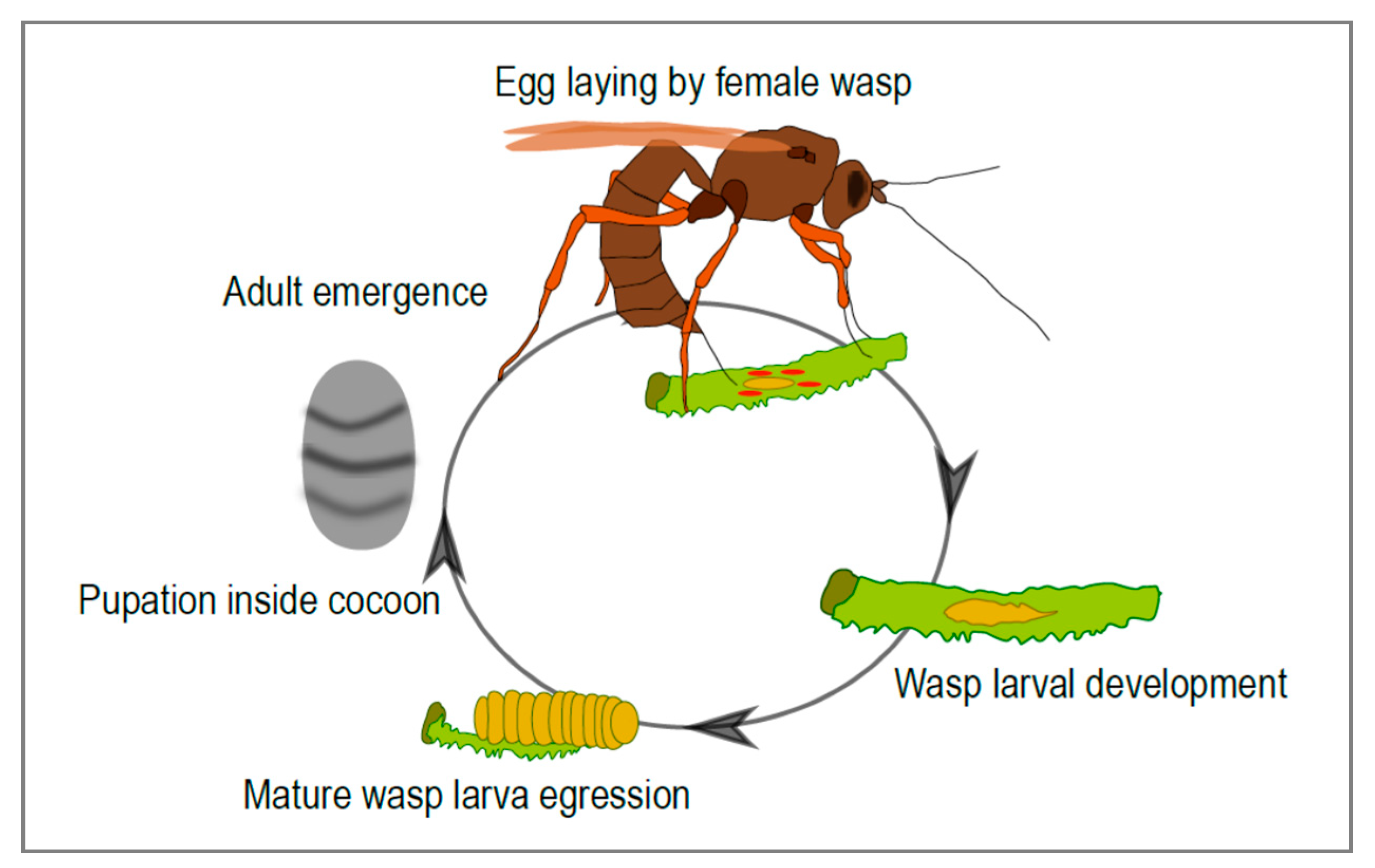
Some wasps are even parasitoids of parasitoids; the eggs of Euceros are laid beside lepidopteran larvae and the wasp larvae feed temporarily on their haemolymph, but if a parasitoid emerges from the host, the hyperparasites continue their life cycle inside the parasitoid. Parasitoids maintain their extreme diversity through narrow specialism.. Workers of the European wasp leave the nest in search of food, and are attracted to meats, sweet food and drink. Life history cycle. European wasp colonies are started in spring by a single fertilised queen, which lays an egg in a number of cells in the nest. These hatch into grub-like larvae and are tended by the queen for a number of weeks.

Pest advice for controlling Wasps
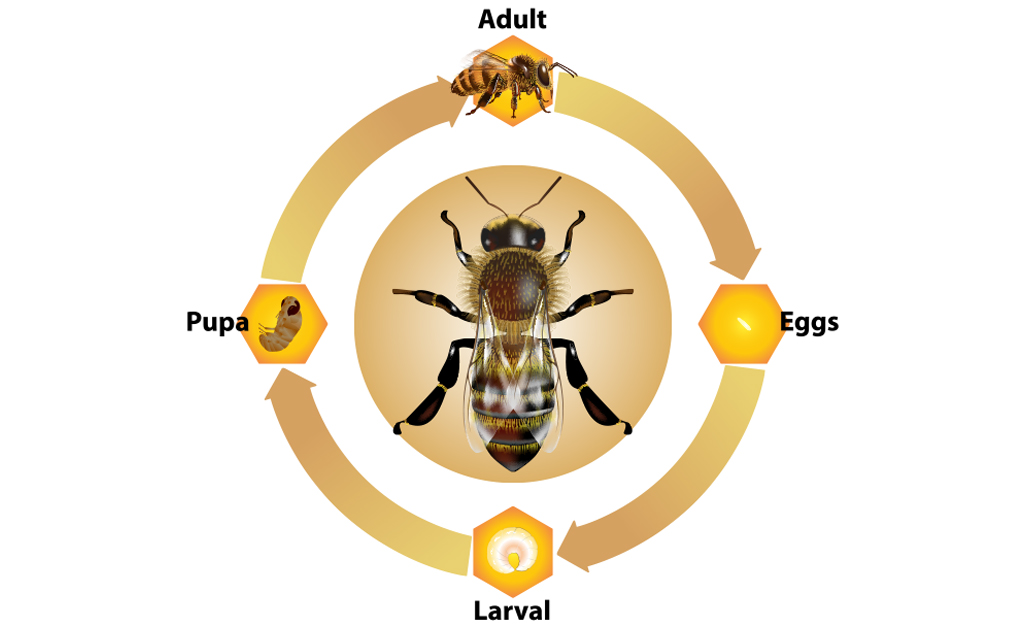
alien Mordrin communication life cycle of wasps nest Persistent Christchurch

How To Get Rid Of European Paper Wasps Control Facts Etc

Fig treewasp life cycle, illustration Stock Image C022/9828 Science Photo Library

Polistes dominula host and Xenos vesparum parasite life cycle.... Download Scientific Diagram

Life cycle of parasitoid wasps and Polydnaviruses (PDVs) parasitizing a... Download Scientific
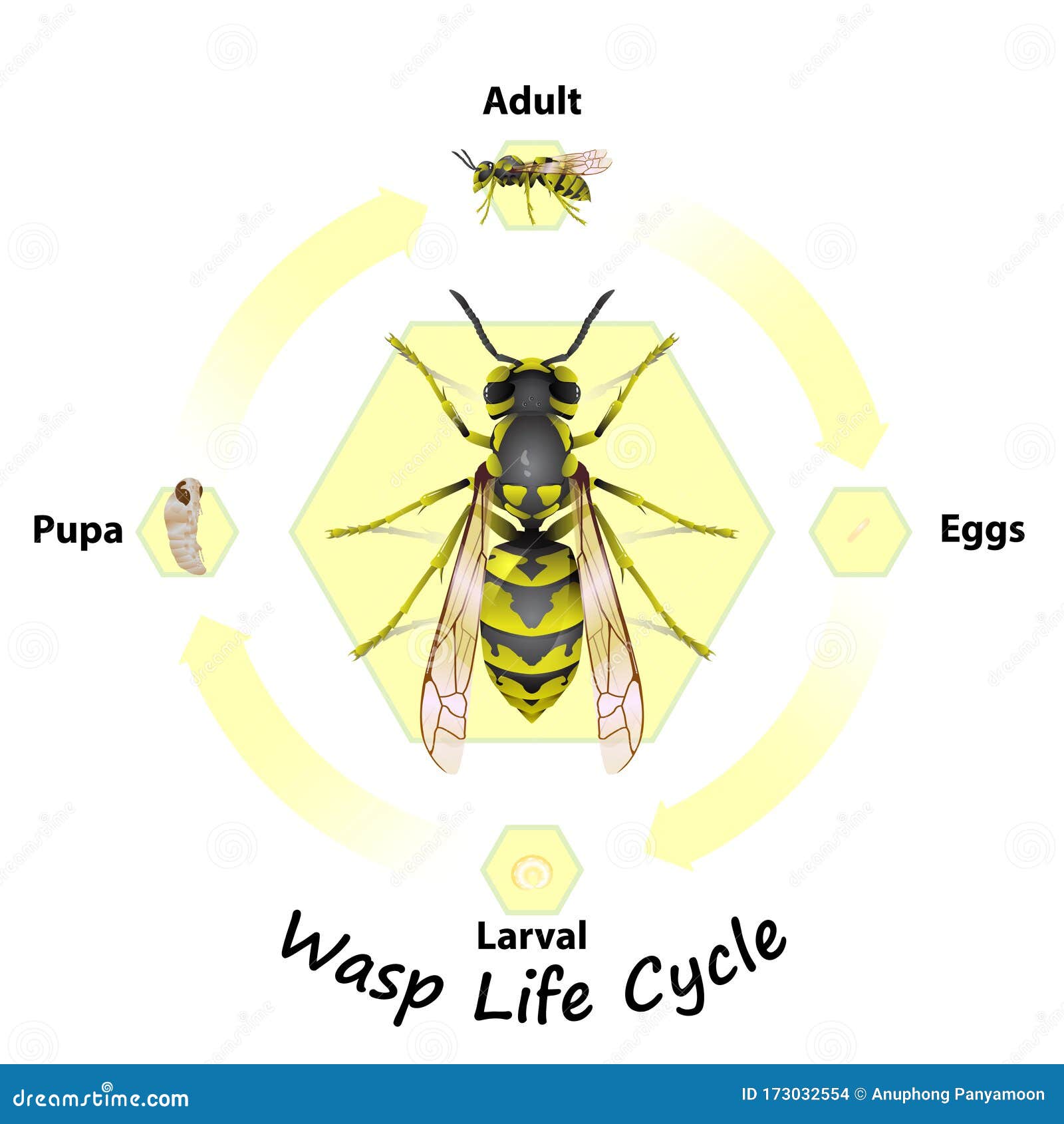
Wasp Life Cycle Vector for Education. Stock Vector Illustration of background, icon 173032554

PPT Do you know what type of relationship your Fig Newton was involved in? PowerPoint

bee life cycle Science Education, Elementary Education, Fun Facts About Bees, Bee Life Cycle

The lifecycle of the strepsipteran Xenos vesparum in parallel with the... Download Scientific

9 Biological cycle of an hymenopteran aphid parasitoid. Modified after... Download Scientific
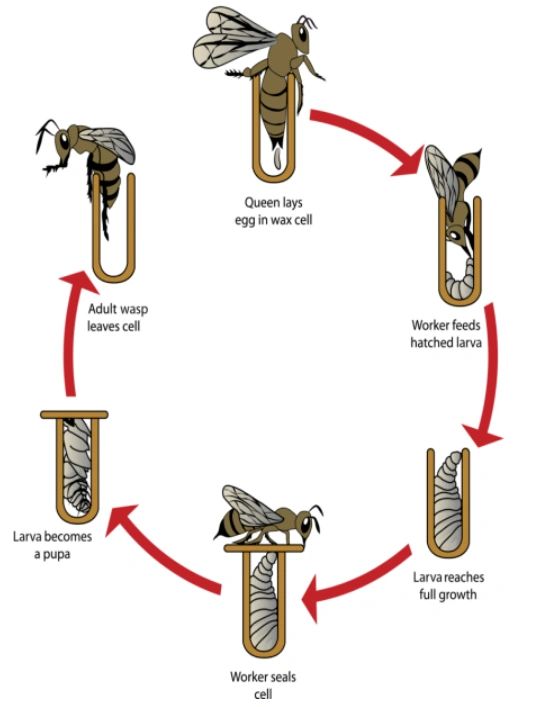
Wasp Life Cycle
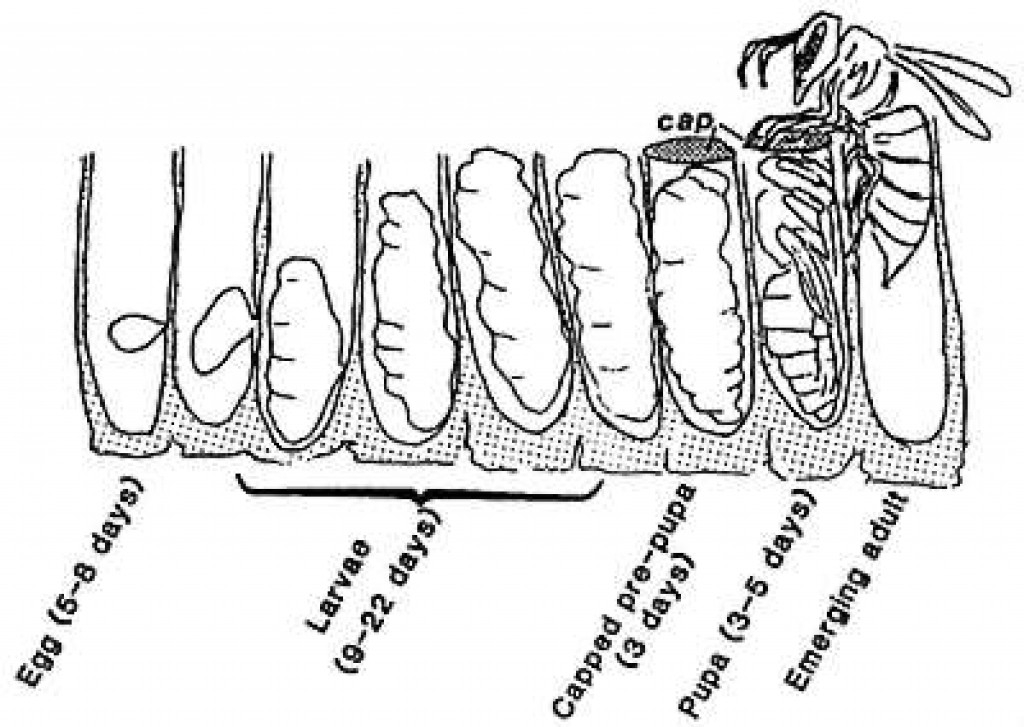
wasp life cycle nz Keena Darling

Life Cycle of Wasps and Pest Supply Canada
Yellow Jacket Wasp Life Cycle
The Wasp Life Cycle When Do Wasps Die Off? Hullternative

Parasitoid wasp life cycle — Science Learning Hub
wasp life cycle uk Whacking Blook Pictures
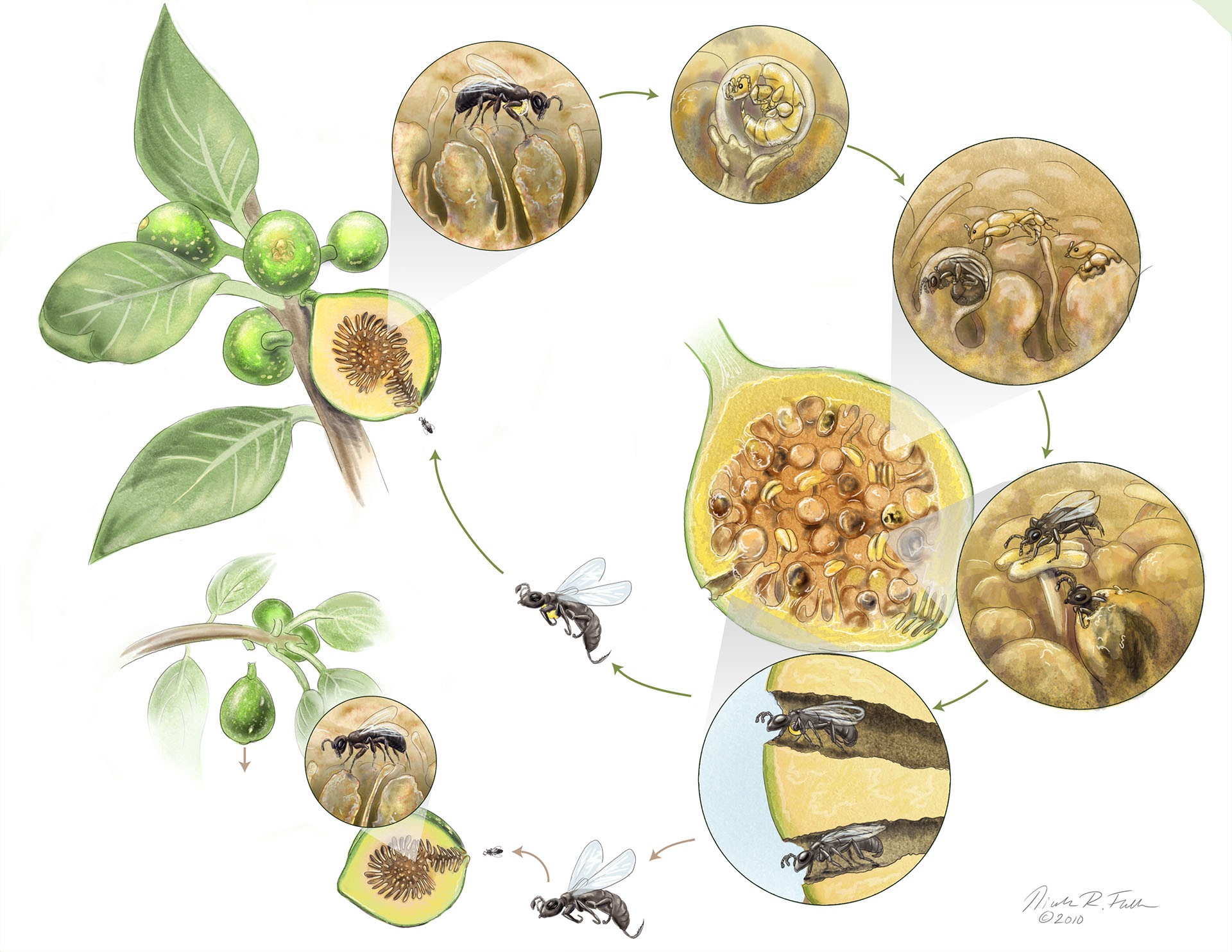
Fig Wasp LifeCycle Portfolio SayoStudio

Population statistics for MdBV proviral segments in the M.... Download Scientific Diagram
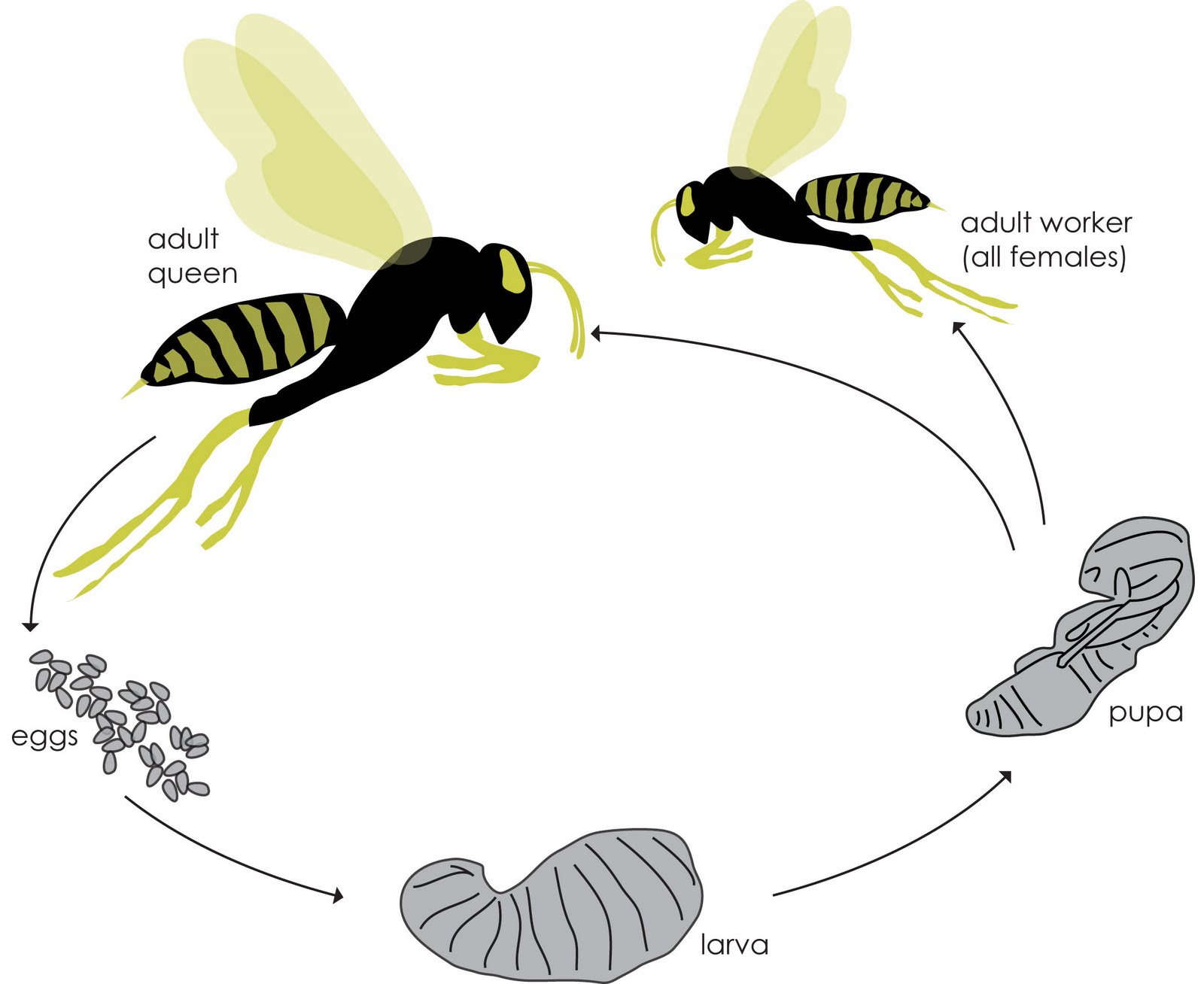
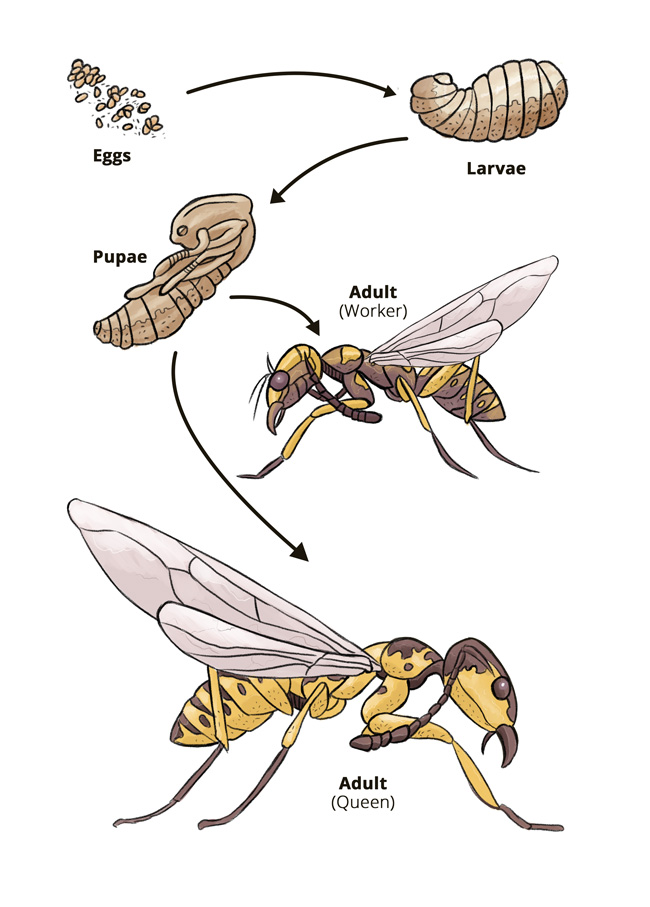
Wasps go through four stages in their life cycle: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. After mating, a new queen wasp flies away to start a new colony in a tree, shrub, or under a building eave. The queen lays eggs in the nest, and the larvae feed on the food provided by their mother. After this stage, they become pupae and then develop as adults.. As there are many different types of wasps, this article focuses on the yellowjacket, one of the most common types of wasp from the Vespidae family. The yellowjacket life cycle begins with a fertile queen, who builds a nest and uses stored sperm to create worker bees. These worker bees continue building the colony, and die off at the end of summer.